Automatic virtual voltage extraction of a 2xN quantum dot array
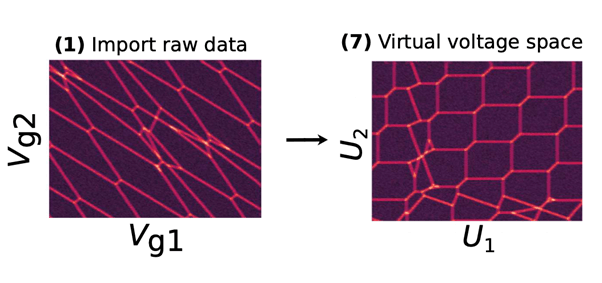
Spin qubits in quantum dots are a compelling platform for fault-tolerant quantum computing due to the potential to fabricate dense two-dimensional arrays with nearest neighbour couplings, a requirement to implement the surface code. However, due to the proximity of the surface gate electrodes cross-coupling capacitances can be substantial, making it difficult to control each quantum dot independently. To automate the process, we successfully train a neural network to extract the gradients from a Hough transformation of a stability diagram and test the algorithm on simulated and experimental data of a 2×2 quantum dot array.
