Integrated readout of silicon quantum dots in a CMOS chip
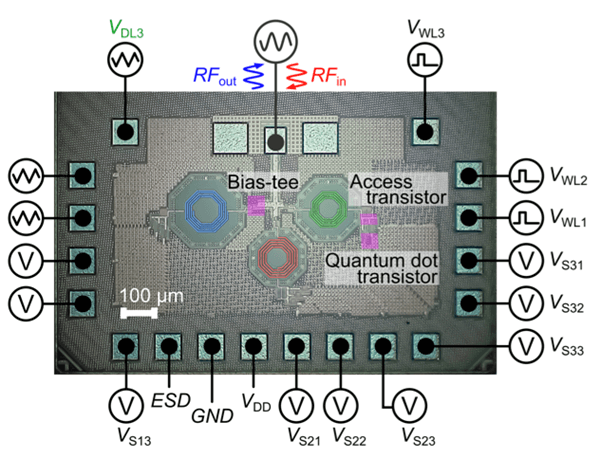
We present a cryogenic integrated circuit (IC) fabricated using industrial CMOS technology that hosts three key ingredients of a silicon-based quantum processor: quantum dot arrays (arranged here in a non-interacting 3×3 configuration), digital electronics to minimize control lines using row-column addressing and analog LC resonators for multiplexed readout, all operating at 50 mK. With the microwave resonators (6-8 GHz range), we show dispersive readout of the charge state of the QDs and perform combined time- and frequency-domain multiplexing, enabling scalable readout while reducing the overall chip footprint. Work performed in collaboration with the group of Edoardo Charbon at EPFL (École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne).
